What is the Cerebellum? 8 Brain Terms You Need To Know
- Education
Share this post on social media


The cerebe-what? Listen, we get it. The brain can be a complicated subject. People spend years learning and understanding this complicated organ. And we are still learning, too! We want to help you understand the basics of the brain on your journey to greater mindfulness.
The brain is one of the largest organs in the human body; it is also the most complex. The brain is made up of more than 100 billion (!) nerves. These nerves are constantly communicating and creating trillions (!!) of connections. Several specialized areas in the brain are all constantly working together—often without us even thinking about it. Here are 8 terms you need to know.

The cerebellum is the second largest part of the brain. It has left and right hemispheres, connected in the middle by the vermis. The main responsibility of the cerebellum is maintaining our balance. For instance, when we turn or jump, it subconsciously evaluates the movement to keep us steady. So the next time you get off a rollercoaster and regain your balance, you can thank your cerebellum.
The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum. The cerebral cortex, on the outside of the cerebrum, processes both sensory and motor information. It also helps with how we think about ourselves and the world around us. Visible Body describes how this tissue is mostly neuron cell bodies, “and its folds and fissures give the cerebrum its trademark rumpled surface.” The cerebral cortex is divided into a left and right hemisphere, which is then divided into the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, and parietal lobe. These lobes help your memory, planning, speech, decisions, and more.
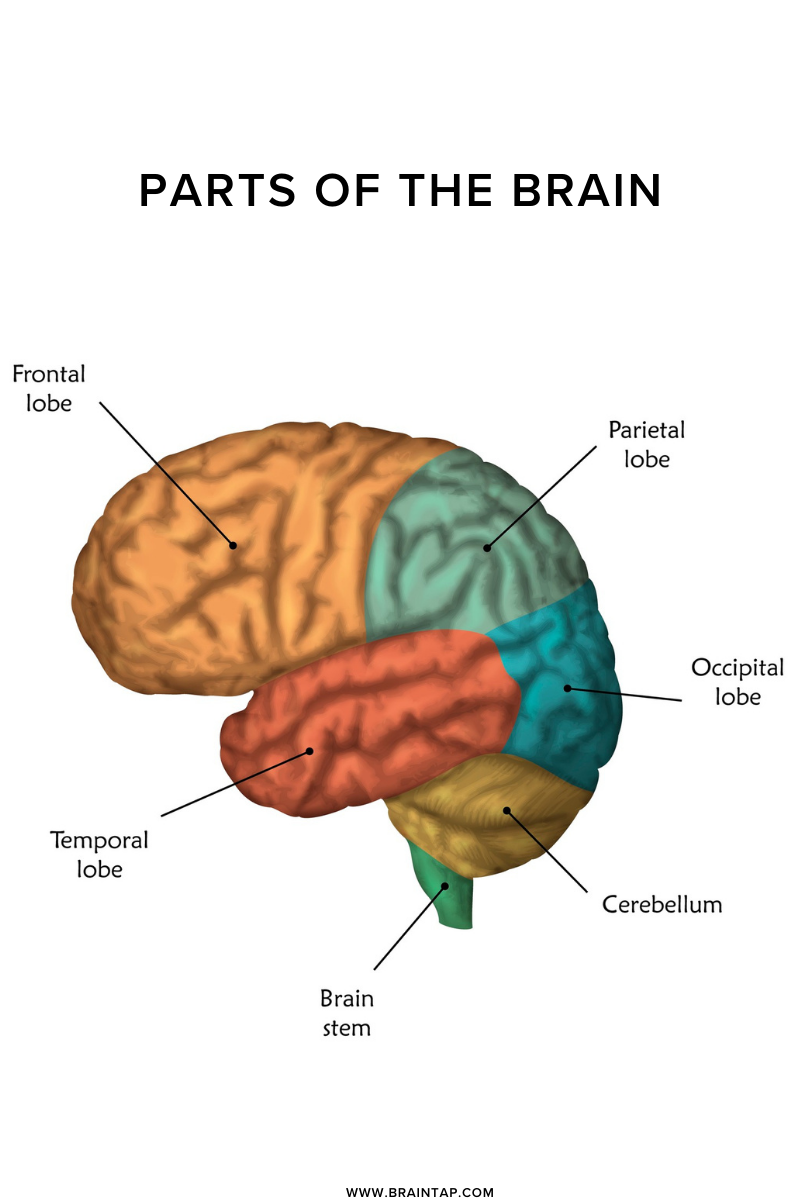
You know when your heart starts to race when you’re about to give a presentation or jump off the diving board? That is your amygdala speaking. The amygdala is in the anterior part of the temporal lobe of the cerebrum, playing an important role in our emotions, behavior, and overall motivation.
We have all experienced the moment we smell something that recalls a distant memory. This is due to the hippocampus in our brain. The hippocampus aids in the forming, organizing, and keeping of memories, while connecting emotions and sensations (like smell) to these memories.
The hypothalamus has an important role to control various bodily functions. Some of its responsibilities include releasing hormones, regulating emotional responses, controlling appetite, regulating temperature, and more.
The brain stem sends signals from the brain and the spinal cord and vice versa. It helps in managing involuntary functions, as well as passing on sensory and motor signals. The brain stem includes the medulla oblongata (helps with respiration, digestion, circulation, swallowing, coughing, etc.), the pons (handles breathing), and the midbrain (aids hearing, sight, and motor functions).
Entrainment refers to the synchronization of organisms to an external rhythm. Brainwave entrainment simulates the rhythms of specific brain wave frequencies to help with relaxation and rejuvenation. To reach deep levels of relaxation, visualization encourages imagination, creativity, and innovation.
According to Science Direct, “Brain waves are oscillating electrical voltages in the brain measuring just a few millionths of a volt.” BrainTap describes these frequencies as the following:

Though complex, the brain is a beautiful tool we have. There are many more terms and definitions to help us better understand this complicated organ; however, how we use our brain is even more important than what we know about it. Focusing on mindfulness and mental health will help you have a stronger, more healthy brain, which in turn affects every aspect of your life.
Elevate your mind: Subscribe to our newsletter for insights on brain health, cutting-edge research updates, and personalized session suggestions to help you unleash your ultimate potential!
We only send what matters—no spam, no sharing. We promise.


Customer Support
In order to streamline support requests and better serve you, we utilize a support ticket system. Every support request is assigned a unique ticket number. Please keep your support ticket number in a safe place and provide your number when contacting us.
Manufacturer’s Warranty
The BrainTap Headset Bluetooth model has a 12-month manufacturer’s warranty that covers any flaws or defects that the headset shipped with. Any sort of sustained physical damage is not covered under warranty. All other products or equipment come with a 30-day manufacturer’s warranty unless otherwise stated. Please reference your User Manual to view the complete warranty policy. Should you experience any difficulty with your equipment or accessories, we recommend first checking the troubleshooting guidelines in the User Manual included with the headset or reference our online Knowledge Base for headset tips and troubleshooting steps. If you are still having trouble and your headset is within the warranty period, call our Help Desk at 302-721-6677 or fill out an online support ticket for further assistance. If the item needs to be returned to BrainTap offices for assessment and replacement, you will be asked to provide proof of purchase and will be issued a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number and shipping instructions. Items without proof of purchase will not be accepted for RMA.
Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) Policy
A Return Merchandize Authorization (RMA) is a numbered authorization provided to permit the return of a product. Any product returned to BrainTap offices for testing, trade-in or refund must be accompanied by an RMA issued by our Help Desk. Please note that RMAs expire 15 days after issue. Returns postmarked after the expiration date will not be accepted. Please be sure to ship your return item promptly.
Out of Warranty Support Options
Should you experience any difficulty with your equipment or accessories, we recommend first checking the troubleshooting guidelines in the User Manual reference our online Knowledge Base for headset tips and troubleshooting steps. Even if your headset is outside of the warranty period, you can reach out to our Help Desk via phone at 302-721-6677 or online by filling out a support ticket for further help. If the product is determined to require replacement after troubleshooting, there is an option for an out of warranty trade-in and replacement for a fee. We do not offer repair services for out of warranty products.
Satisfaction Guarantee & Equipment Return Policy
There is a 45-day return policy on all products and packages purchased directly from BrainTap unless otherwise stated. BrainTap headsets purchased from a retail outlet or 3rd party must be returned to the place of purchase and are subject to the return policy of the seller. All returns must have proof of purchase and a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number or the return will not be accepted. All products returns are subject to a 15% restocking fee. The return period begins on the day you received your order. To initiate the return process, reach out to our Help Desk via phone at 302-721-6677 or submit an online support ticket.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees, if any, including duties and import taxes for international shipments, are non-refundable. In all instances, return shipping fees are the responsibility of the purchaser.
Membership Subscriptions
You may cancel your membership/program/subscription with a 30-day notice by logging into your account on BrainTap.com. Click the account icon at the top right of the page, then click the profile icon on the top right-hand side and then click Billing. Once you are on the Billing page you will be able to “Manage Subscriptions & Payment” where you can cancel your subscription.
All subscribers are required to provide a 30-day cancellation notice prior to terminating their subscription. This policy is implemented to ensure a smooth transition for both subscribers and the service provider, allowing for adequate time to process cancellation requests and manage subscription changes.
Calculation of 30-Day Notice Period: The 30-day cancellation notice period will be calculated from the next monthly payment due date following the receipt of the cancellation request. For example, if a subscriber submits a cancellation request on the 5th of the month and their next monthly payment is due on the 15th of the same month, the 30-day notice period will commence from the 15th of the month and extend until the 15th of the following month. Free trials are exempt from this 30-day notice policy and may be canceled at any time prior to the first payment due date without payment or penalty.
Refund Processing Time
It takes approximately 10 – 14 days to process a return. If you have any questions regarding your refund, refer / respond to your original support ticket or create a new support ticket and one of our customer support representatives will contact you.
Terms and Conditions of Use:
Last updated: January 30, 2024
This is an agreement between you and BrainTap, Inc. (with its affiliates, “BrainTap”, “we” or “us”) regarding the digital audio-recorded motivational programs and creative visualization sessions operated by BrainTap Technologies (the “Service”). Additionally, please read the site’s Privacy Policy.
By signing up for or using the Service, you agree to the following terms:
Your Account
If you do not have a BrainTap membership, you will need to establish an account with BrainTap.com to use the Service. Your payment methods on file with your BrainTap.com account will be used for your BrainTap account and the BrainTap Brain Fitness mobile application.
Membership/Programs/Subscription Plans
By subscribing to BrainTap’s mobile app, users are granted access to use the app on up to two devices. Each device is permitted up to five plays per day. The BrainTap Brain Fitness mobile app subscription is intended for personal use only. Commercial use in a business is strictly prohibited unless said business has an official Professional Partner License issued by BrainTap, Inc. BrainTap reserves the right to modify the subscription terms and limitations at any time without prior notice. Users are encouraged to review the terms periodically for any updates or changes. If you sign up for a membership/program/subscription plan, you agree to the terms, conditions and limitations associated with them that are posted on our websites or applications.
Promotional and Membership/Program/Subscription Content
We may make content available to you from time to time through the Service for which a purchase is not required. You will have access to this content only for so long as we make it available generally or, where it is provided as a benefit of a membership plan, for so long as you remain an active member of your plan in good standing. We may also remove this content from your account, devices and applications, or otherwise restrict your ability to access it.
Content Availability
We may add or remove purchasable, promotional and membership content (collectively, “Content”) from our catalog, membership plans and our Service at any time and make no guarantee as to the availability of specific Content in any membership plan or as to any minimum amount of Content in any membership plan. Some of our Content may be offered in limited territories or to limited membership levels. We may use geo-filtering technology to restrict access outside of those territories.
Fees and Renewal
Fees for purchased program content, membership plans, subscriptions, and other services will be stated at the time of your purchase or sign-up, as applicable, and provided in our help pages. The fees for membership plans may vary. Fees may be subject to tax and are non-refundable unless otherwise outlined herein. We only accept credit card and (most) debit cards for payment of membership fees. Please do not sign up for a program with a “check” or “ATM” card.
If your membership plan or subscription involves a recurring payment of a fee, unless you notify us 30 days before a charge that you want to cancel or do not want to automatically renew your membership or subscription, you understand it will automatically continue each month, and you authorize us (without notice to you, unless required by applicable law) to collect the then-applicable fees and any taxes using any credit card we have on record for you. All cancellations require a 30-day notice to allow time for processing.
If all credit cards we have on file for you are declined for payment of your membership or subscription fees, we may cancel your membership or subscription, as applicable, unless you provide us with a new credit card. If you provide us with a new credit card and are successfully charged before your membership or subscription is cancelled, your new membership or subscription period will be based on the original renewal date and not the date of the successful charge.
Membership/Program/Subscription Cancellation
You may cancel your membership/program/subscription with a 30-day notice by logging into your account on BrainTap.com. Click the account icon at the top right of the page, then click the profile icon on the top right-hand side and then click Billing. Once you are on the Billing page you will be able to “Manage Subscriptions & Payment” where you can cancel your subscription.
All subscribers are required to provide a 30-day cancellation notice prior to terminating their subscription. This policy is implemented to ensure a smooth transition for both subscribers and the service provider, allowing for adequate time to process cancellation requests and manage subscription changes.
Calculation of 30-Day Notice Period: The 30-day cancellation notice period will be calculated from the next monthly payment due date following the receipt of the cancellation request. For example, if a subscriber submits a cancellation request on the 5th of the month and their next monthly payment is due on the 15th of the same month, the 30-day notice period will commence from the 15th of the month and extend until the 15th of the following month. Free trials are exempt from this 30-day notice policy and may be canceled at any time prior to the first payment due date without payment or penalty.
Service Restrictions
We reserve the right to accept or refuse membership or to restrict use of the Service at our discretion. You may not transfer or assign your membership or any Service benefits. You may not use the Service for any commercial purposes without a written license to do so. If you would like to use any of the Services in a business setting, please contact us for information. We may take actions we deem reasonably necessary to prevent fraud and abuse, including placing restrictions on the amount of content or other services that can be accessed from the Service at any one time.
Content Restrictions
All content is protected by Federal copyright law. You may not (i) transfer, copy, share, or display Content, except as permitted in this Agreement; (ii) sell, rent, lease, distribute, or broadcast any Content; (iii) remove any proprietary notices or labels on Content; (iv) attempt to disable, bypass, modify, defeat, or otherwise circumvent any digital rights management or other protection system applied to Content or used as part of the Service; or (v) use the Service or Content for any commercial or illegal purpose.
Promotional Trial Memberships
We sometimes offer certain customers various trial or other promotional memberships, which are subject to the Terms except as otherwise stated in the promotional offers. We reserve the right, in our sole discretion, to determine your eligibility. Trial members may, at any time (through your “My Account”), choose not to continue paid memberships/subscriptions by cancelling prior to the end of the trial period. If a trial offer or a promotion requires you to have a valid payment instrument on file, such as a credit card or other permitted payment method, we may validate that payment method, including by requesting a temporary authorization from the financial institution issuing your payment instrument. If we determine that your payment instrument is invalid, without limiting any of our other rights, we may revoke any benefits, Credits or Content you may have received as part of the offer.
Agreement Changes
We may, at our discretion, change the Terms and all elements of them and any aspect of the Service without notice to you. If any change to the Terms is found invalid, void, or for any reason unenforceable, that change is sever-able and does not affect the validity and enforce-ability of any remaining changes and the remainder of the Terms. Your continued use of the Service after we change the Terms constitutes your acceptance of the changes. If you do not agree to any changes, you must not use the Service and must cancel your membership.
Termination by Us
Our business may change over time and we reserve the right to cancel the Service and any membership plan in whole or in part, and to terminate your membership and use of the Service at our discretion without notice. If we do so, we will give you a prorated refund based on the number of days remaining in your membership unless we terminate your membership for conduct that we determine, in our discretion, violates the Terms, violates any applicable law, involves fraud or misuse of the Service, or is harmful to our interests or another user. Our failure to insist upon or enforce your strict compliance with the Terms will not constitute a waiver of any of our rights.
Acceptance of terms of use and amendments
Each time you use or cause access to this website or any BrainTap application, you agree to be bound by these Terms of use, as amended from time to time with or without notice to you. In addition, if you are using a particular service on this website or accessed via this website, you will be subject to any rules or guidelines applicable to those services, and they will be incorporated by reference within these Terms of use. Additionally, please read the site’s Privacy policy and Warranty and Return policy if applicable.
The site editor’s service
This website and the services provided to you on and via this website are provided on an “AS IS” basis. You agree that the site editor reserves the right to modify or discontinue provision of this website and its services, and to remove the data you provide, either temporarily or permanently, at any time, without notice and without any liability towards you. The site editor will not be held responsible or liable for timeliness, removal of information, failure to store information, inaccuracy of information, or improper delivery of information.
Your responsibilities and registration obligations
In order to use this website, certain parts of it, or our mobile application, you may be required to register for a user account on this website; in this case, you agree to provide truthful information when requested, and — if a minimum age is required for eligibility for a user account — you undertake that you are at least the required age. By registering for a user account, you explicitly agree to this site’s Terms of use, including any amendments made by the site editor that are published herein.
Registration and password
You are responsible for maintaining the confidentiality of your password, and you will be responsible for all usage of your user account and/or user name, whether authorized or not authorized by you. You agree to immediately notify the site editor of any unauthorized use of your user account, username or password.
Your conduct
You agree that all information or data of any kind, whether text, software, code, music or sound, photographs or graphics, video or other materials (“content”), made available publicly or privately, will be under the sole responsibility of the person providing the said content, or of the person whose user account is used. You agree that this website may expose you to content that may be objectionable or offensive. The site editor will not be responsible to you in any way for content displayed on this website, nor for any error or omission.
By using this website or any service provided, you explicitly agree that:
(a) you will not provide any content or conduct yourself in any way that may be construed as: unlawful; illegal; threatening; harmful; abusive; harassing; stalking; tortuous; defamatory; libelous; vulgar; obscene; offensive; objectionable; pornographic; designed to interfere with or disrupt the operation of this website or any service provided; infected with a virus or other destructive or deleterious programming routine; giving rise to civil or criminal liability; or in violation of an applicable local, national or international law;
(b) you will not impersonate or misrepresent your association with any person or entity; you will not forge or otherwise seek to conceal or misrepresent the origin of any content provided by you;
(c) you will not collect or harvest any information about other users;
(d) you will not provide, and you will not use this website to provide, any content or service in any commercial manner, or in any manner that would involve junk mail, spam, chain letters, pyramid schemes, or any other form of unauthorized advertising or commerce; you will not use this website to promote or operate any service or content without the site editor’s prior written consent;
(e) you will not provide any content that may give rise to the site editor being held civilly or criminally liable, or that may be considered a violation of any local, national or international law, including — but not limited to — laws relating to copyrights, trademarks, patents, or trade secrets.
Submission of content on this website
By providing any content to this website:
(a) you agree to grant the site editor a worldwide, royalty-free, perpetual, non-exclusive right and license (including any moral rights or other necessary rights.) to use, display, reproduce, modify, adapt, publish, distribute, perform, promote, archive, translate, and to create derivative works and compilations, in whole or in part. Such license will apply with respect to any form, media, technology already known at the time of provision or developed subsequently;
(b) you warrant and represent that you have all legal, moral, and other rights that may be necessary to grant the site editor the license specified in this section;
(c) you acknowledge and agree that the site editor will have the right (but not obligation), at the site editor’s entire discretion, to refuse to publish, or to remove, or to block access to any content you provide, at any time and for any reason, with or without notice.
Third-party services
Goods and services of third parties may be advertised and/or may be made available on or through this website. Representations made regarding products and services provided by third parties will be governed by the policies and representations made by these third parties. The site editor will not in any manner be liable for or responsible for any of your dealings or interaction with third parties.
Indemnification
You agree to indemnify and hold harmless the site editor and the site editor’s representatives, subsidiaries, affiliates, related parties, officers, directors, employees, agents, independent contractors, advertisers, partners, and co-branders, from any claim or demand, including reasonable legal fees, that may be filed by any third party, arising out of your conduct or connection with this website or our services, including by not limited to services provided via our mobile application(s), your provision of content, your violation of these Terms of use, or any other violation by you of the rights of another person or party.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
YOU UNDERSTAND AND AGREE THAT YOUR USE OF THIS WEBSITE AND OF ANY SERVICES OR CONTENT PROVIDED (THE “SERVICE”) IS AT YOUR OWN RISK. SERVICES AND CONTENT ARE PROVIDED TO YOU “AS IS”, AND THE SITE EDITOR EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EITHER IMPLIED OR EXPRESS, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANT-ABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, AND NON-INFRINGEMENT.
THE SITE EDITOR MAKES NO WARRANTY, EITHER IMPLIED OR EXPRESS, THAT ANY PART OF THE SERVICE WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED, ERROR-FREE, VIRUS-FREE, TIMELY, SECURE, ACCURATE, RELIABLE, OR OF ANY QUALITY, NOR IS IT WARRANTED EITHER IMPLICITLY OR EXPRESSLY THAT ANY CONTENT IS SAFE IN ANY MANNER FOR DOWNLOAD. YOU UNDERSTAND AND AGREE THAT NEITHER THE SITE EDITOR NOR ANY PARTICIPANT IN THE SERVICE PROVIDES PROFESSIONAL ADVICE OF ANY KIND AND THAT ANY ADVICE OR ANY OTHER INFORMATION OBTAINED VIA THIS WEBSITE MAY BE USED SOLELY AT YOUR OWN RISK, AND THAT THE SITE EDITOR WILL NOT BE HELD LIABLE IN ANY WAY.
Some jurisdictions may not allow disclaimers of implied warranties, and certain statements in the above disclaimer may not apply to you as regards implied warranties; the other terms and conditions remain enforceable notwithstanding.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
YOU EXPRESSLY UNDERSTAND AND AGREE THAT THE SITE EDITOR WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR EXEMPLARY DAMAGES; THIS INCLUDES, BUT IS NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, GOODWILL, USE, DATA OR OTHER INTANGIBLE LOSSES (EVEN IF THE SITE EDITOR HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES), RESULTING FROM (I) THE USE OF SERVICES OR THE INABILITY TO USE SERVICES, (II) THE COST OF OBTAINING SUBSTITUTE GOODS AND/OR SERVICES RESULTING FROM ANY TRANSACTION ENTERED INTO ON THROUGH SERVICES, (III) UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS TO OR ALTERATION OF YOUR DATA TRANSMISSIONS, (IV) STATEMENTS BY ANY THIRD PARTY OR CONDUCT OF ANY THIRD PARTY USING SERVICES, OR (V) ANY OTHER MATTER RELATING TO SERVICES.
In some jurisdictions, it is not permitted to limit liability and, therefore, such limitations may not apply to you.
Reservation of rights
The site editor reserves all of the site editor’s rights, including but not limited to any and all copyrights, trademarks, patents, trade secrets, and any other proprietary right that the site editor may have in respect to this website, its content, and goods and services that may be provided. The use of the site editor’s rights and property requires the site editor’s prior written consent. By making services available to you, the site editor is not providing you with any implied or express licenses or rights, and you will have no rights to make any commercial use of this website or provided services without the site owner/editor’s prior written consent.
Notification of copyright infringement
If you believe that your property has been used in any way that could be considered a copyright infringement or a violation of your intellectual property rights, the site editor’s copyright agent may be contacted via:
e-mail to the site administrator
Applicable law
You agree that these Terms of use and any dispute arising out of your use of this website or products or services provided will be governed by and construed in accordance with local laws applicable at the site editor’s domicile, notwithstanding any differences between the said applicable legislation and legislation in force at your location. By registering for a user account on this website, or by using this website and the services it provides, you accept that jurisdiction is granted to the courts having jurisdiction over the site editor’s domicile, and that any disputes will be heard by the said courts.
Miscellaneous information
(i) In the event that any provision of these Terms of use is deemed to conflict with legislation by a court with jurisdiction over the parties, the said provision will be interpreted to reflect the original intentions of the parties in accordance with applicable law, and the remainder of these Terms of use will remain valid and applicable; (ii) The failure of either party to assert any right under these Terms of use will not be considered to be a waiver of that party’s right, and the said right will remain in full force and effect; (iii) You agree that any claim or cause in respect of this website or its services must be filed within one (1) year after such claim or cause arose, or the said claim or cause will be forever barred, without regard to any contrary legislation; (iv) The site editor may assign the site editor’s rights and obligations under these Terms of use; in this event, the site editor will be relieved of any further obligation.
We know that you care how your information is used, and we appreciate your trust that we will use it carefully and sensibly. This notice describes our privacy policy. By visiting us, you are accepting the privacy policy described below.
1. What Personal Information Do We Collect?
2. How Do We Use Your Information?
3. How Do We Protect the Security of Your Information?
4. Your Choice: Opt-in or Opt-out. It is your choice whether to receive emails or special offers from us or others. The following section provides you with this choice. Please note the default settings.
5. Children: We do not sell products or services to children. If you are under 18, you may use this site only with involvement of a parent or guardian.
6. Other Websites: Various Web sites may be linked to from this site. If you link to another site, your privacy depends on the policy of that site. We strongly urge you to check their privacy policy. Not all sites guarantee that they will not share your personally identifiable information with others. You may also wish to consult privacy guidelines such as those recommended by the Online Privacy Alliance (www.privacyalliance.org).
7. Contact Us: If you would like to learn more about our privacy policy, or to access your personally identifiable information contained on our website, you may contact us via the Contact Us page. You will be required to provide identifier information to assure that this information is not released to others. We reserve the right to modify this policy in the future. If we do so, notice will be posted on our home page.